Pinpoint Your SolarWinds Exposure with Cisco Endpoint Security Analytics
The anyconnect ask command specifies how the anyconnect client will be installed on the user’s computer. The none default anyconnect part tells the ASA not to ask the user if he/she wants to use WebVPN or anyconnect but just starts the download of the anyconnect client automatically. The anyconnect dpd-interval command is used for Dead Peer. The university’s virtual private network (VPN) is designed to allow individuals to securely 'tunnel' into campus over personal and public networks, such as a home Wi-Fi network, and access services as if they were on campus. The VPN, powered by Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility, is a quick and easy way to securely connect to the FSU network. Cisco AnyConnect client features are enabled in AnyConnect profiles. These profiles can contain configuration settings like server list, backup server list, authentication time out, etc., for client VPN functionality, in addition to other optional client modules like Network Access Manager, ISE posture, customer experience feedback, and web. Cisco AnyConnect - Empower your employees to work from anywhere, on company laptops or personal mobile devices, at any time. AnyConnect simplifies secure endpoint access and provides the security necessary to help keep your organization safe and protected. Feb 05, 2020 Obtain Cisco AnyConnect VPN client log from the client computer using the Windows Event Viewer. Choose Start Run and type eventvwr.msc /s. Locate the Cisco AnyConnect VPN Client in the Applications and Services Logs (of Windows 7) and choose Save Log File As. Assign a filename, for example, AnyConnectClientLog.evt.
With Cisco Endpoint Security Analytics (CESA) in your toolkit, you can quickly assess your own exposure and address endpoint visibility gaps left behind by traditional EDR/EPP solutions and network security analytics platforms.
How to Monitor VPN Split Tunneling and Remote Endpoints with Existing Infrastructure
Learn how Cisco Endpoint Security Analytics (CESA) helps alleviate VPN bandwidth constraints while improving endpoint security for remote work deployments.
Cisco and Splunk Technology Innovations Showcase at Splunk .Conf19, Vegas, 2019
Cisco-Splunk partnership is growing at a terrific pace. Recently, Splunk showcased Cisco as one of its top 4 partners. As a testimony to our growing momentum, Cisco is a Peta sponsor this year at Splunk .conf19, Venetian sands, Las Vegas, Oct 21-25.
Using CESA to Solve Endpoint Blindness for a World Class InfoSec Team
Cisco Endpoint Security Analytics (CESA) Built on Splunk brings together the endpoint behavioral visibility of Cisco’s AnyConnect Network Visibility Module (NVM) and the data transformation power of Splunk analytics.
Find What Your Endpoint Anti-Malware is Missing with CESA Built on Splunk
Splunk’s analytics-driven security solutions are a perfect complement to Cisco Security. This partnership has generated CESA Built on Splunk, which is a solution unlike anything available in the industry.
A Cisco & Splunk Security Integration Everyone Should Be Using
Shining a light on an integration that is among the most powerful of all our Splunk integrations – Cisco AnyConnect Network Visibility Module and its associated Splunk app.
It’s Time to Turn Your Access Control Perimeter into a Threat Control Perimeter
Is your security ‘Game Plan’ reactive or proactive? Firms need to up their offensive game and strategy to evolve network perimeter security from just access control to effective threat control.
Developing Network Security in the DevNet Sandbox
This is what DevNet sandbox is all about. Providing access to real world security environments where one can see first-hand how these integrations work.
Cisco and Splunk Demonstrate the Power of Integration
You already know that insights from data are the foundation for digital business. Much of this data comes directly from your data center, network and security infrastructures. But let’s face it, using custom-built or disparate tools to analyze each system is challenging at best. This is where Cisco and Splunk can help. Cisco and Splunk […]
Objective
The objective of this document is to show you how to configure AnyConnect VPN connectivity on the RV34x Series Router.
Advantages of using AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client:
- Secure and persistent connectivity
- Persistent security and policy enforcement
- Deployable from the Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) or from Enterprise Software Deployment Systems
- Customizable and translatable
- Easily configured
- Supports both Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Supports Internet Key Exchange version 2.0 (IKEv2.0) protocol
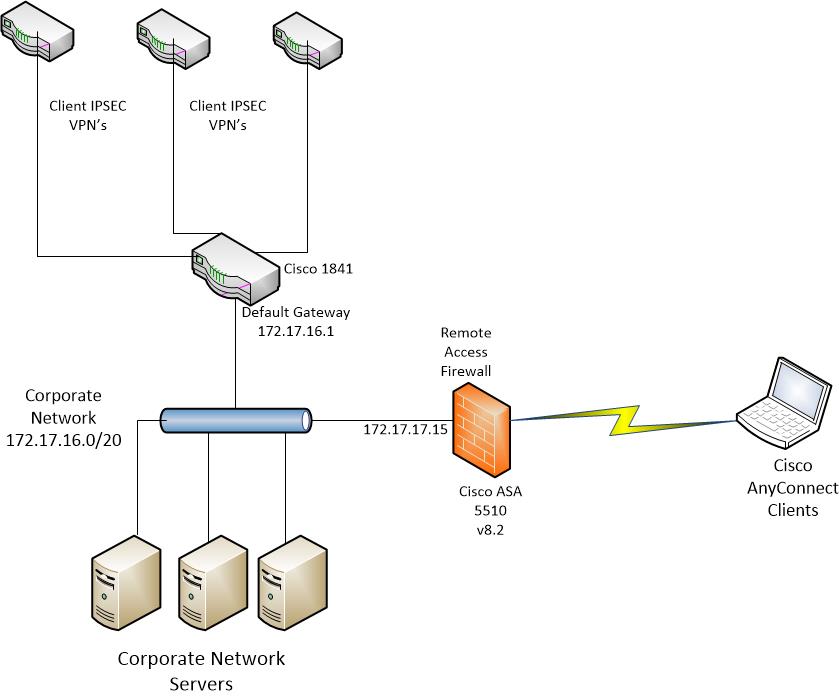
Introduction
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection allows users to access, send, and receive data to and from a private network by means of going through a public or shared network such as the Internet but still ensuring secure connections to an underlying network infrastructure to protect the private network and its resources.
A VPN client is software that is installed and ran on a computer that wishes to connect to the remote network. This client software must be set up with the same configuration as that of the VPN server such as the IP address and authentication information. This authentication information includes the username and the pre-shared key that will be used to encrypt the data. Depending on the physical location of the networks to be connected, a VPN client can also be a hardware device. This usually happens if the VPN connection is used to connect two networks that are in separate locations.
The Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client is a software application for connecting to a VPN that works on various operating systems and hardware configurations. This software application makes it possible for remote resources of another network become accessible as if the user is directly connected to his network, but in a secure way. Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client provides an innovative new way to protect mobile users on computer-based or smart-phone platforms, providing a more seamless, always-protected experience for end users and comprehensive policy enforcement for IT administrator.
On the RV34x router, starting with firmware version 1.0.3.15 and moving forward, AnyConnect licensing is not necessary. There will be a charge for client licenses only.
For additional information on AnyConnect licensing on the RV340 series routers, please see the article on: AnyConnect Licensing for the RV340 Series Routers.
Applicable Devices | Firmware Version
- Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client | 4.4 (Download latest)
- RV34x Series | 1.0.03.15 (Download latest)
Cisco Anyconnect Vpn Client Download
Configure AnyConnect VPN Connectivity on the RV34x
Configure SSL VPN on the RV34x
Step 1. Access the router web-based utility and choose VPN > SSL VPN.
Step 2. Click the On radio button to enable Cisco SSL VPN Server.
Mandatory Gateway Settings
The following configuration settings are mandatory:
Step 3. Choose the Gateway Interface from the drop-down list. This will be the port that will be used for passing traffic through the SSL VPN Tunnels. The options are:
- WAN1
- WAN2
- USB1
- USB2
Note: In this example, WAN1 is chosen.
Cisco Anyconnect Windows 10
Step 4. Enter the port number that is used for the SSL VPN gateway in the Gateway Port field ranging from 1 to 65535.
Note: In this example, 8443 is used as the port number.
Step 5. Choose the Certificate File from the drop-down list. This certificate authenticates users who attempt to access the network resource through the SSL VPN tunnels. The drop-down list contains a default certificate and the certificates that are imported.
Note: In this example, Default is chosen.
Step 6. Enter the IP address of the client address pool in the Client Address Pool field. This pool will be the range of IP addresses that will be allocated to remote VPN clients.
Note: Make sure that the IP address range does not overlap with any of the IP addresses on the local network.
Note: In this example, 192.168.0.0 is used.
Step 7. Choose the Client Netmask from the drop-down list.
Note: In this example, 255.255.255.128 is chosen.
Step 8. Enter the client domain name in the Client Domain field. This will be the domain name that should be pushed to SSL VPN clients.
Note: In this example, WideDomain.com is used as the client domain name.
Step 9. Enter the text that would appear as login banner in the Login Banner field. This will be the banner that will be displayed each time a client logs in.
Note: In this example, Welcome to Widedomain! is used as the Login Banner.
Optional Gateway Settings
The following configuration settings are optional:
Step 1. Enter a value in seconds for the Idle Timeout ranging from 60 to 86400. This will be the time duration that the SSL VPN session can remain idle.
Note: In this example, 3000 is used.
Step 2. Enter a value in seconds in the Session Timeout field. This is the time it takes for the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) session to time out after the specified idle time. The range is from 60 to 1209600.
Note: In this example, 60 is used.
Step 3. Enter a value in seconds in the ClientDPD Timeout field ranging from 0 to 3600. This value specifies the periodic sending of HELLO/ACK messages to check the status of the VPN tunnel.
Note: This feature must be enabled on both ends of the VPN tunnel.
Note: In this example, 350 is used.
Step 4. Enter a value in seconds in the GatewayDPD Timeout field ranging from 0 to 3600. This value specifies the periodic sending of HELLO/ACK messages to check the status of the VPN tunnel.
Note: This feature must be enabled on both ends of the VPN tunnel.
Note: In this example, 360 is used.
Step 5. Enter a value in seconds in the Keep Alive field ranging from 0 to 600. This feature ensures that your router is always connected to the Internet. It will attempt to re-establish the VPN connection if it is dropped.
Note: In this example, 40 is used.
Step 6. Enter a value in seconds for the duration of the tunnel to be connected in the Lease Duration field. The range is from 600 to 1209600.
Note: In this example, 43500 is used.
Step 7. Enter the packet size in bytes that can be sent over the network. The range is from 576 to 1406.
Note: In this example, 1406 is used.
Step 8. Enter the relay interval time in the Rekey Interval field. The Rekey feature allows the SSL keys to renegotiate after the session has been established. The range is from 0 to 43200.
Note: In this example, 3600 is used.
Step 9. Click Apply.
Configure Group Policies
Step 1. Click the Group Policies tab.
Step 2. Click the Add button under the SSL VPN Group Table to add a group policy.
Note: The SSL VPN Group table will show the list of group policies on the device. You can also edit the first group policy on the list, which is named SSLVPNDefaultPolicy. This is the default policy supplied by the device.
Step 3. Enter your preferred policy name in the Policy Name field.
Note: In this example, Group 1 Policy is used.
Cisco Anyconnect Download
Step 4. Enter the IP address of the Primary DNS in the field provided. By default, this IP address is already supplied.
Note: In this example, 192.168.1.1 is used.
Step 5. (Optional) Enter the IP address of the Secondary DNS in the field provided. This will serve as a backup in case the primary DNS failed.
Note: In this example, 192.168.1.2 is used.
Step 6. (Optional) Enter the IP address of the primary WINS in the field provided.
Note: In this example, 192.168.1.1 is used.
Step 7. (Optional) Enter the IP address of the secondary WINS in the field provided.
Note: In this example, 192.168.1.2 is used.
Step 8. (Optional) Enter a description of the policy in the Description field.
Cisco Anyconnect Admin Guide
Note: In this example, Group Policy with split tunnel is used.
Step 9. (Optional) Click on a radio button to choose the IE Proxy Policy to enable Microsoft Internet Explorer (MSIE) proxy settings to establish VPN tunnel. The options are:
- None - Allows the browser to use no proxy settings.
- Auto - Allows the browser to automatically detect the proxy settings.
- Bypass-local - Allows the browser to bypass the proxy settings that are configured on the remote user.
- Disabled - Disables the MSIE proxy settings.
Note: In this example, Disabled is chosen. This is the default setting.
Step 10. (Optional) In the Split Tunneling Settings area, check the Enable Split Tunneling check box to allow Internet destined traffic to be sent unencrypted directly to the Internet. Full Tunneling sends all traffic to the end device where it is then routed to destination resources, eliminating the corporate network from the path for web access.
Step 11. (Optional) Click on a radio button to choose whether to include or exclude traffic when applying the split tunneling.

Note: In this example, Include Traffic is chosen.
Step 12. In the Split Network Table, click the Add button to add split Network exception.
Step 13. Enter the IP address of the network in the field provided.
Note: In this example, 192.168.1.0 is used.
Step 14. In the Split DNS Table, click the Add button to add split DNS exception.
Step 15. Enter the Domain name in the field provided and then click Apply.
Verify AnyConnect VPN Connectivity
Step 1. Click on the AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client icon.
Step 2. In the AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client window, enter the gateway IP address and the gateway port number separated by a colon (:), and then click Connect.
Note: In this example, 10.10.10.1:8443 is used. The software will now show that it is contacting the remote network.
Step 3. Enter your server username and password in the respective fields and then click OK.
Note: In this example, Group1 user is used as the Username.
Step 4. As soon as the connection is established, the Login Banner will appear. Click Accept.
The AnyConnect window should now indicate the successful VPN connection to the network.
Step 5. (Optional) To disconnect from the network, click Disconnect.
You should now have successfully configured AnyConnect VPN connectivity using an RV34x Series Router.
View a video related to this article...




