There are some classic theories and practical circuits that describe a FET as Voltage Variable Resistor (FET as VVR). You can use commonly used FET such as BFW10/11 or any available to you as a. The evaluation procedure presented the reliability of equipment VVR-ts and the results of calculations with and without considering the opinion of the.
Table of Contents - 123456789RS¬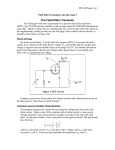 ®
®Threshold voltage, VT, is the voltage required to fully deplete the doped channel layer:
Two regions:
quadratic region where the depletion layer is less than the channel thickness d
saturated region where the depletion layer at the drain end equals the channel thickness d
The drain current become independent of the drain voltage and equals:
Fet As Vvr And Its Application
Fig.8.x Drain current versus Drain-Source voltage at a gate-source voltage of 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 0.8 and 1.0 Volt for a silicon JFET with built-in potential of 1 V. Channel parameters and device dimensions are listed in the table below.
Channel width | W | 1 mm |
Channel length | L | 1 mm |
| mn | 100 cm2/V-s |
Channel doping | Nd | 1017 cm-3 |
Channel thickness |
|
|
Built-in potential | fi | 1 V |
Table 8.x JFET parameters
The transfer characteristic of a JFET is shown in the figure below and compared to a quadratic expression of the form
where is the average depletion layer width in the channel layer. The quadratic expression yields the same current at VG = fi for = 3d/8.

Fig.8.x Transfer characteristic of a JFET. Shown is the square root of the drain current of the JFET (solid line) and a quadratic fit with =3d/8.
Introduction:
The following section will explain in details about the FET as a Voltage Variable Resistor-(VVR).
Fet As Vvr
FET as a Voltage Variable Resistor-(VVR):
Fet As Vvr In Vca
- FET is a device that is usually operated in the constant-current portion of its output characteristics.
- But if it is operated on the region prior to pinch-off (that is where VDS is small, say below 100 mV), it will behave as a voltage-variable resistor (WE).
- It is due to the fact that in this region drain-to-source resistance RDS can be controlled by varying the bias voltage VGS.
- In such applications the FET is also referred to as a voltage-variable resistor or volatile dependent resistor.
- It finds applications in many areas where this property is useful.
- Figure shows the drain characteristic curves for a 2N 5951 in the ohmic region (i.e. for low VDS).
- From the characteristic curve it can be seen that RDS varies with VGS. For example, when VGS = 0, RDS = 133 ohm and when VGS = – 2 V, RDS = 250 ohm.
- Because of this a JFET operating in the ohmic region with small ac signals acts as a voltage-controlled resistance.
- Note that the drain curves shown in figure, extend on both sides of the origin.
- This means that a JFET can be employed as a voltage-variable resistor for small ac signals, typically those less than 100 mV.
- When it is employed in this way, it does not require a dc drain voltage from the supply. All that is required is an ac input signal.




